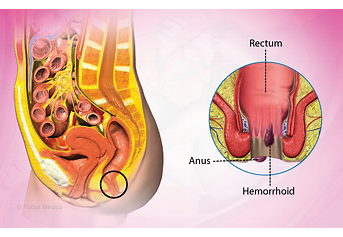
Piles, also known as hemorrhoids, are swollen veins in the lower rectum or anus. They can cause discomfort, pain, and bleeding, making daily activities challenging. However, with the right treatment and lifestyle adjustments, managing piles becomes much easier.
Causes of Piles
Several factors contribute to the development of piles, including:
- Chronic constipation or diarrhea
- Straining during bowel movements
- Sitting for prolonged periods
- Pregnancy, due to increased pressure on the pelvic veins
- Obesity and lack of physical activity
- Low-fiber diet leading to hard stools
Common Symptoms
Piles can present with a variety of symptoms, depending on their severity. Some common signs include:
- Itching or irritation around the anus
- Pain or discomfort, especially while sitting
- Swelling or lumps near the anal region
- Bright red blood during bowel movements
- Mucus discharge after passing stool
If these symptoms persist, consulting a doctor is essential to prevent complications.
Types of Piles
Piles are classified into two main types:
- Internal Piles – Located inside the rectum, they usually don’t cause pain but may lead to bleeding.
- External Piles – Found under the skin around the anus, they can be painful and may develop blood clots.
Piles Treatment Options
The treatment approach depends on the severity of the condition. Here are some effective options:
Lifestyle and Dietary Changes
- Increase fiber intake through fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Drink plenty of water to soften stools.
- Avoid straining during bowel movements.
- Exercise regularly to improve digestion and circulation.
Medical and Minimally Invasive Treatments
If lifestyle changes don’t provide relief, medical interventions may be required:
- Medications – Ointments, creams, and suppositories help reduce swelling and discomfort.
- Rubber Band Ligation – A small band is placed around the hemorrhoid to cut off blood supply, causing it to shrink.
- Sclerotherapy – A chemical injection shrinks the hemorrhoid tissue.
- Infrared Coagulation – Heat is used to shrink internal piles.
Surgical Treatment
For severe cases, surgery might be necessary. The most common procedures include:
- Hemorrhoidectomy – Surgical removal of large or recurring piles.
- Stapler Hemorrhoidectomy (PPH) – A modern technique that reduces pain and recovery time.
- Laser Surgery – A minimally invasive procedure that offers faster healing with minimal discomfort.
When to See a Doctor
If piles persist despite home remedies or if there is excessive bleeding, severe pain, or infection, seeking medical advice is crucial. Early intervention prevents complications and ensures a quicker recovery.
Conclusion
Piles can be uncomfortable, but effective treatment options are available. With a proper diagnosis and the right medical approach, relief is possible. If you’re experiencing persistent symptoms, consult Dr. Nayar for expert guidance and personalized care.
